Blog
Dental hygiene tips for healthy teeth & gums
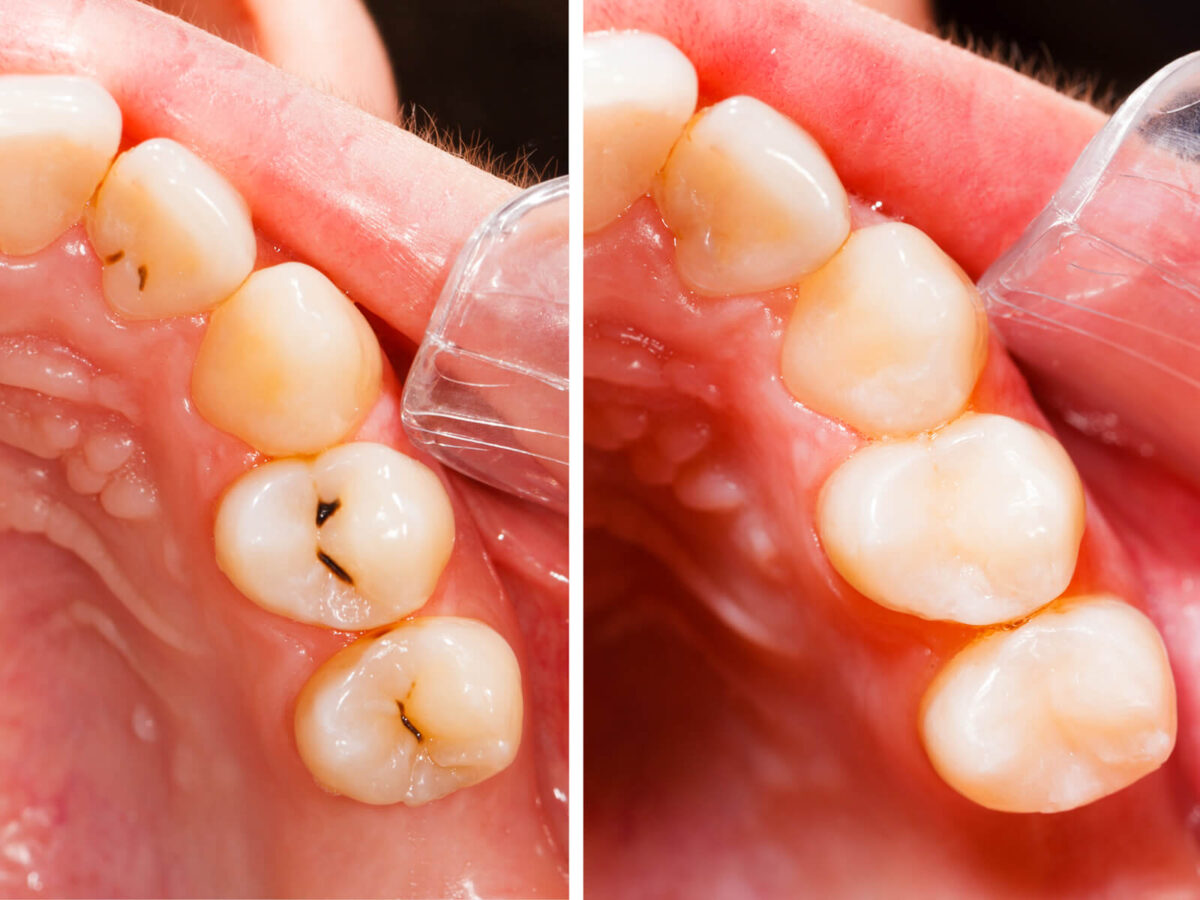
All You Need To Know About Cavities And Fillings
People of all ages often experience cavities. Knowing the causes and treatments of cavities is important for maintaining oral health. In addition, dentists frequently use fillings to restore teeth damaged by cavities. The following is some information on cavities and fillings that you should know to better understand tooth restoration treatments.
What Are Cavities or Dental Caries?
Cavities, which are alternatively referred to as dental caries, are the permanent damaging points found on the hard surface of your teeth that develop into small openings or gaps. This is because they are caused by various things, including bacteria in your mouth, too much snacking, poor oral hygiene, and sugary drinks.
Causes of Cavities
Plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, causes cavities. The acids produced by the bacteria present in the plaque will make tooth enamel erode. These acids, over time, will lead to tiny holes in the enamel that result in cavities. Some factors that contribute to cavity formation include:
Poor Oral Hygiene: Failure to brush or floss encourages the growth of a sticky substance called plaque which if left on the teeth will cause acids to attack the outer cover of the teeth known as enamel.
Frequent Snacking and Sugary Drinks: Sweets and other products containing high amounts of both sugar and acids in the mouth create a constant feed for bacteria, therefore increasing the opportunities to develop cavities.
Dry Mouth: Saliva helps to cleanse food debris and micro-organisms which we take in our daily diet and if one experiences dry mouth, it could be as a result of illnesses or the use of certain drugs that contribute to the formation of cavities.
Eating Disorders: Stomach acid weakens the tooth’s enamel through regular exposure, which is common in conditions such as anorexia and bulimia hence causing cavities.
Signs and Symptoms of Cavities
Cavities may not cause noticeable symptoms initially. However, as they grow, you may experience:
- Toothache: Persistent pain in the affected tooth.
- Sensitivity: Discomfort when eating or drinking something hot, cold, or sweet.
- Visible Holes or Pits: Noticeable openings or pits in the affected tooth.
- Staining: Brown, black, or white staining on the surface of the tooth.
- Pain When Biting: Discomfort or pain when chewing or biting down.
Tooth Restoration: The Role of Fillings
Tooth restoration through fillings is often needed when a cavity forms. Fillings are used to restore the function and integrity of the tooth, preventing further decay. Here’s how it works:
Diagnosis: During an examination of your teeth at a dental check-up, your dentist may take X-rays to identify cavities.
Preparation: The affected area will be numbed by the dentist using a local anesthetic so that you don’t feel any pain during the procedure. Then, using a drill or laser, the decayed portion of the tooth is removed.
Filling the Cavity: Once caries are dissolved, the dentist removes the cavity and rinses to eliminate bacteria and other materials. Then, he or she condenses it with the right substance e.g. composite resin, amalgam, gold, or porcelain.
Shaping and Polishing: The filling is modeled to correspond to the physical impression of the tooth and polished so that the surface is smooth to the applying forces during the chewing.
Types of Filling Materials
Different materials can be used in tooth restoration, each with its advantages and disadvantages:
Composite Resins: These blend well with natural teeth, hence their use as white filling materials. They are suitable for small to medium-sized restorations but may not have much durability compared with other materials.
Amalgam: These are silver-filling materials that are strong enough to stay for a long time in one’s mouth, as they do not easily get damaged.
Gold: Gold fillings are long-lasting and durable, although they are more expensive than other filling materials and require multiple visits.
Porcelain: Porcelain fillings are custom-made in a laboratory to bond to the tooth. They look very natural and do not wear off easily. However, they can be expensive.
Preventing Cavities
Prevent cavities by practicing good oral hygiene and making healthy choices. Below are some tips:
Brushing And Flossing Regularly: Brush your teeth at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and floss once a day to remove plaque as well as food particles.
Maintaining a Healthy Diet: Limit your intake of sugary or acidic foods and drinks, for example, soda pop, candy, etc. Have a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, dairy, etc.
Regular Dental Check-ups: Schedule visits to the dentist and have the teeth and mouth area professionally cleaned more often. Regular checkups should be done because it is easier to treat a cavity before other severe dental issues form.
Using Fluoride: It makes teeth more resistant to pressure or cavities since it is a compound that helps strengthen the outer surface of teeth, known as the enamel. According to dentists, this product should only be used externally in the toothpaste form along with supplements.
Conclusion
Understanding cavities and the significance of tooth restoration through fillings is essential for retaining proper oral health. Recognizing the signs of cavities and searching for prompt dental care can save your smile. Practicing precise oral hygiene, having a balanced food plan, and frequently visiting your dentist are key to stopping cavities and ensuring long-term dental health. Don’t wait for a toothache to remind you to take care of your enamel—start today and enjoy a healthier and brighter smile.


