Blog
Dental hygiene tips for healthy teeth & gums
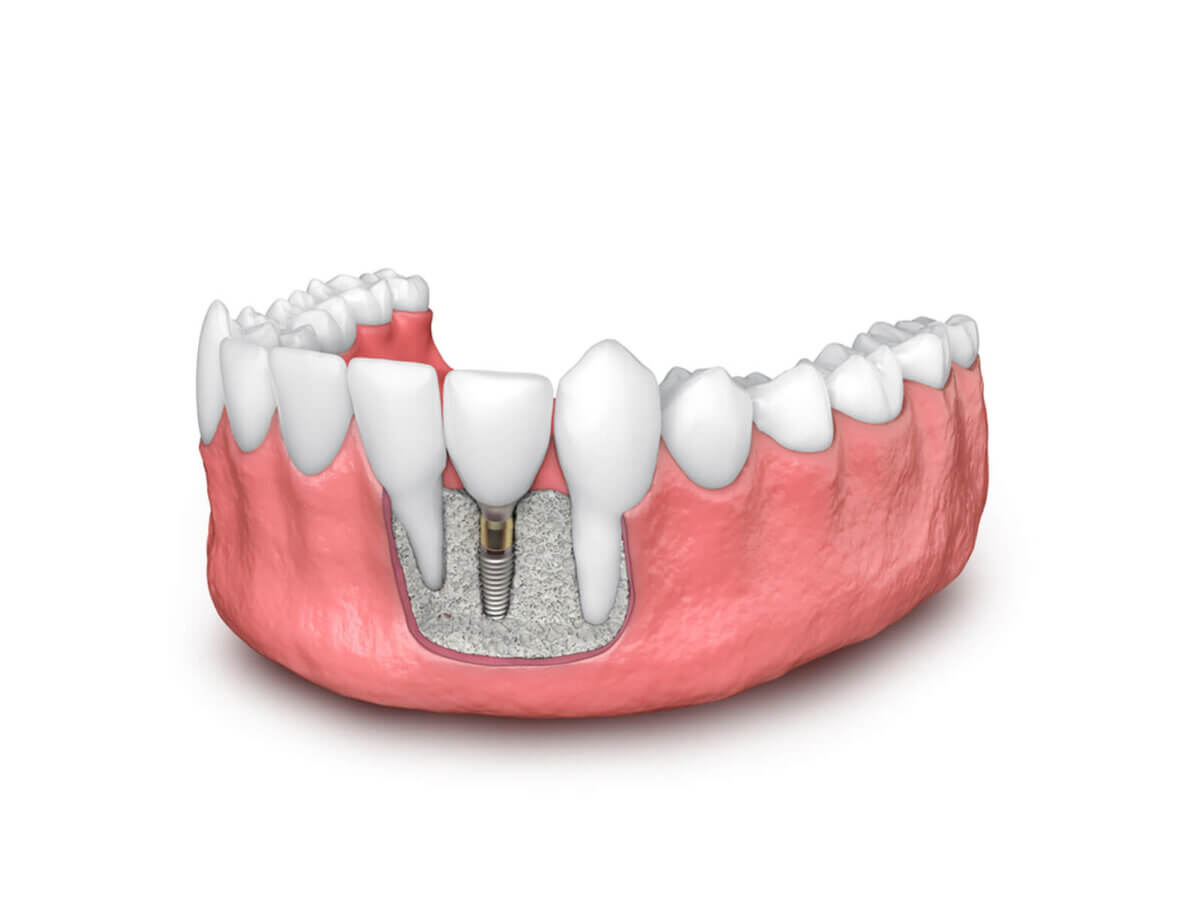
Dental Implants And Bone Health: Understanding Bone Grafting
Dental implants have revolutionized tooth replacement by providing a durable and long-lasting alternative. However, successful implantation depends on the health and density of the jawbone. Dental practitioners may propose bone grafting to strengthen the foundation for successful implants when the bone volume is insufficient.
This article dives into the critical relationship between dental implants and bone health, focusing on the significance of bone grafting treatments in ensuring effective placement.
Relationship Between Dental Implants And Bone Health
1. Osseointegration:
- Definition: Helps improve stability by fusing the implant with the jawbone, simulating the natural tooth-root connection.
- Dependence on Bone Quality: The success of osseointegration is determined by the quality and amount of existing jawbone.
2. The impact of tooth loss:
- Bone Resorption: When a tooth is lost, the jawbone in that area may resorb, reducing bone volume.
- Reduced bone density impairs the stability of possible dental implants.
3. Bone Grafting as a Solution
- Augmenting Bone Volume: Bone grafting transfers bone material to a deficient location to increase volume and create a solid implant foundation.
- Promoting Osseointegration: Grafted bone acts as a scaffold, promoting osseointegration and extending the life of dental implants.
Understand Bone Grafting Procedures:
1. Types of Bone Grafts:
- Autografts are bone materials derived from the patient’s body, typically from the hip or jaw.
- Allografts are pieces of bone donated by another person that have been carefully treated to eliminate any cells.
- Xenografts are another type where bone from animals, typically bovine or porcine, can be used as xenografts following processing.
2. Bone Grafting Process:
- Location Preparation: Prepare the implant location and remove any damaged or inadequate bone to produce a clean space.
- Graft Placement: The selected graft material is carefully implanted in the prepared site, covering any flaws or shortcomings.
- Healing Period: The graft goes through a healing period in which it fuses with the surrounding bone, boosting regeneration.
3. Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR):
A barrier membrane over the graft site limits soft tissue ingrowth and promotes bone regeneration. The membrane controls bone regrowth, ensuring the grafting procedure’s success.
Benefits and Considerations for Bone Grafting:
1. Increased Implant Success:
- Bone grafting considerably improves the support offered to dental implants, assuring their long-term durability.
- Minimizing Complications: Adequate bone volume lowers the likelihood of complications such as implant failure or looseness.
2. Improved Aesthetics:
- Grafting preserves the natural curves of the jaw and facial structure, avoiding the sunken appearance caused by bone loss.
- Optimal Gum Appearance: Adequate bone support promotes natural-looking gums around the implant, improving overall appearance.
3. Customisation for Individuals:
- Dentists can customize bone grafting techniques based on individual needs, including graft material and augmentation level.
- Predictable Outcomes: Advances in grafting techniques and materials have resulted in more predictable outcomes, raising the success percentage of dental implant treatments.
Recovery and aftercare:
1. Patient Compliance: For best healing, patients should follow specified rules after grafting.
Monitoring Progress: Regular check-ups enable dental practitioners to track the progression of bone regeneration.
2. Timing Considerations: Dental specialists choose the best time for implant placement based on the patient’s healing status and the readiness of the augmented bone.
Seamless Integration: Implants are implanted after the graft fully integrates, ensuring a smooth transition.
Conclusion
The success of dental implants depends on the quality of the jawbone. Bone grafting is a critical treatment for people with low bone volume, providing the support required for successful implantation. Various grafting materials and processes enable personalized approaches, resulting in predictable outcomes that improve functional and aesthetic features.
As implant dentistry advances, bone grafting remains a cornerstone technique, aiding the integration of dental implants and laying the groundwork for enduring smiles.


